- Membership & Community
-
Publications & News
- Physiology Journals
-
Newsroom
-
The Physiologist Magazine
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2022
- 2023
- 2024
-
In Depth
- In Depth—The Bear Necessities
- In Depth: Understanding Circadian Rhythms
- In Depth: Understanding Data
- In Depth: Exercise Physiology: Take Your Medicine at the Gym
- In Depth: Neurodegenerative Disorders
- Imaging Methods Unveil the Invisible
- Rewiring the Brain: Breakthroughs in Neural Therapy
- What’s Coming Next for GLP-1 and Metabolic Disease Treatment
- Understanding the Effects of Maternal Exercise
- How Muscles May Hold Cues to Better Sleep
- The Science Behind Breathwork and Mental Health
-
Mentoring Forum
- Net Worth
- Take Care
- You … In Charge
- Work. It. Out.
- Working Off-site
- Location, Location, Location?
- Student Support
- Progressing to Postdoc
- Relationship Building
- Let’s Get It Started
- What Do We Value?
- It’s a Postdoc Life
- Coronavirus Contributions
- Creative Communications
- Selection Process
- Conference Connections
- Postdoc Appreciation
- Research Rewards
- Focus on Teaching
- Industry Insights
- Balance Beam
- Post Postdoc
- If You Build It
- Talk It Through
- Forward Bound
- I’ve Earned My PhD. Now What?
- University Life
- Tips for Trainees
- Time Travel
- Prepare Now for the Career You Want
- Landing a Postdoctoral Researcher Position
- Becoming a Physician-Scientist
- Mastering the Art of Science Communication
- Setting Yourself Up for Success in the Lab
- From Postdoc to Professor: Key Strategies for Success
- How to Stay Motivated in Challenging Times
- Staying Motivated Throughout Your Science Career
- Managing Stress and Workload During Your PhD
- Stay Passionate About Your Physiology Career
-
Policy IQ
- Policy IQ—2023 in Review: How APS Advocated on Behalf of Physiologists
- Policy IQ—Supporting Equitable Research
- NIH's Road Map to a Better Postdoc Experience
- The Career Path to Science Advocacy
- Culture of Safety: Stopping Sexual Misconduct
- Physiologists Return to Capitol Hill
- Tips for Scientists to Communicate about Animal Research
- Science Advocacy in a New Political Landscape
- Tips for Making the Call to Congress
- Science Spending Is an Investment
- Advocacy Up Close and Personal
- How Animal Research Advances Physiology and Medicine
-
Publish with Polish
- Publish with Polish
- The Layers of Open Science
- Take Your Content From Meeting to Manuscript
- APS Journals to Highlight Women’s Health Research
- What Subscribe to Open Means for APS Members
- The 5 Pillars of Publish with Purpose
- 3 Types of Metadata Researchers Should Know About
- Navigating Open Access and New Licensing Options
- Journal Manuscript Prep Made Easy
- How to Navigate Public Access Requirements
- Ensuring Public Trust in Publishing
- Improve Your Scientific Figures With APS and BioRender
-
Under the Microscope
- Equine Inspiration
- Inquiring Minds
- The Power of Teaching
- The Love of Physiology
- Understanding Women's Physiology Across the Lifespan
- Studying Human Health in Extreme Environments
- Advancing Kidney Health and Physiology Research
- How Gut Microbes Shape Blood Pressure and Drug Response
- Battling Malaria
- Exploring the Microbiome
- From Physics to Physiology: A Scientist's Unconventional Journey
- Mentoring Q&A
- Evolution
- Baseline by Scott Steen, CAE, FASAE
- 2025
- Find Us on Social Media
-
The Physiologist Magazine
-
Professional Development
-
Meetings & Events
-
American Physiology Summit
- #APS2024 Overview
- Abstracts
- Awards at the Summit
- Award Lectures
- Career Networking Lunch Form
- Dates and Deadlines
- Advocate for Health Research Funding
- Hotel Information
- International Travel Information for Summit Attendees
- Industry Partners
- Keynote Speaker—James Rothman, PhD
- Keynote Speaker—George Brooks, PhD, FAPS
- Keynote Speaker—Holly Ingraham, PhD
- Mobile App
- NIH and NSF Program Officer Panel Discussion Form
- Physical Poster Information
- American Physiology Summit PhysioHub
- Registration
- Section & Group Banquet Tickets
- Social Events
- Speaker Audiovisual Instructions
- Summit FAQs
- Summit Newsroom
- Travel & Transportation
- Undergraduate Program Book
- Liability Waiver
- Industry Partners
- Joseph Erlanger: Pioneering Nerve Research and APS Leadership
- 2023
- 2024
- Scientific Integrity Policy
- Exhibitor Registration Form
- Keynote Speaker Tracy L. Bale, PhD
- Keynote Speaker Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, PhD
- New Trends in Sex Differences and Women’s Health Research
- Control of Renal Function in Health and Disease
- Comparative Physiology Conference
- Webinars
- Related Meetings
- Future APS Conferences
- Conference Policies
-
American Physiology Summit
- APS Awards
-
Career & Professional Development
-
Career Gateway
-
Resources
- Transcript—Leading Through Conflict and Difficult Conversations
- Transcript—Managing Conflict with Colleagues
- Transcript—Leading a Team Through Conflict
- Transcript—Providing Difficult Feedback
- Transcript—Team Dynamics and Culture Primer
- Transcript—Building a Team
- Transcript—Leading a Team Assigned to You
- Transcript—Creating a Team Culture
-
Resources
- Career Navigator
- Center for Physiology Education
- Virtual Courses
- Physiology Job Board
- APS Graduate Physiology & Biomedical Science Catalog
-
Career Gateway
-
Meetings & Events
-
Advocacy & Resources
- Science Policy
-
Resources
- Researcher Resources
- Educator Resources
- Trainee Resources
- Student Resources
-
APS Graduate Physiology & Biomedical Science Catalog
- Des Moines University
- George Washington University
- Michigan State University
- New York Medical College
- Nova Southeastern University
- Pennsylvania State University
- Texas A&M University
- Texas A&M University Medical Physiology
- Stony Brook University
- University of Alabama at Birmingham
- University at Buffalo
- University of Colorado
- University of Michigan
- University of Minnesota
- University of Missouri-Biomedical Sciences
- University of Nebraska Medical Center
- University of Nevada, Reno
- University of South Carolina School of Medicine
- University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC)
- University of Texas Health Science Center
- Virginia Commonwealth University
- Wayne State University
- Physiology Department Catalog Submission Form
- Boston University
- Career Gateway
- Major Initiatives
- About APS
Study suggests daily prune consumption may reduce osteoporosis risk after menopause
 Philadelphia (April 2, 2022)—A study in postmenopausal people suggests eating nutrient-rich prunes every day may be beneficial to bone health, reducing inflammatory factors that contribute to osteoporosis. The research will be presented this week in Philadelphia at the American Physiological Society’s (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2022.
Philadelphia (April 2, 2022)—A study in postmenopausal people suggests eating nutrient-rich prunes every day may be beneficial to bone health, reducing inflammatory factors that contribute to osteoporosis. The research will be presented this week in Philadelphia at the American Physiological Society’s (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2022.
An estimated 13.6 million people in the U.S. over the age of 50 will develop osteoporosis—a loss of bone strength caused by reduced mineral density of the bones—by the year 2030. Osteoporosis increases the risk of fracture, especially in older adults. People who experience menopause have lower levels of estrogen, which trigger an increase in inflammation in the body, which can also contribute to bone loss.
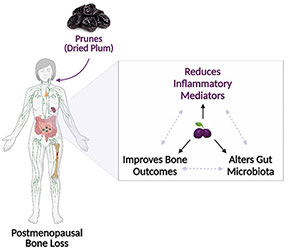
Previous research has shown that polyphenol extracts—plant compounds that act as antioxidants and reduce inflammation—in prunes promote lower levels of oxidative stress and inflammation in a type of bone cell called osteoclasts. In a new study, researchers from the Integrative and Biomedical Physiology Program and the Departments of Nutritional Sciences and Kinesiology at The Pennsylvania State University explored the effects of prunes on bone health after menopause.
Postmenopausal women with a bone mineral density score that was defined as low—a marker of osteoporosis—were divided into three groups:
- One group ate 50 grams (g) of prunes (about six prunes) daily for 12 months.
- A second group ate 100 g of prunes (about 12 prunes) daily for 12 months.
- A control group ate no prunes.
The research team looked at blood samples taken from all volunteers before and after the trial and found significant reductions in inflammatory markers in both of the prune-eating groups compared to the control group.
“Our findings suggest that consumption of six to 12 prunes per day may reduce pro-inflammatory mediators that may contribute to bone loss in postmenopausal women. Thus, prunes might be a promising nutritional intervention to prevent the rise in inflammatory mediators often observed as part of the aging process,” said Janhavi Damani, MS, first author of the study.
NOTE TO JOURNALISTS: To schedule an interview with a member of the research team, or request the abstract, “A randomized controlled trial of dietary supplementation with prunes (dried plums) on inflammatory markers in postmenopausal women,” please contact APS Media Relations or call 301.634.7314. Find more research highlights in our Newsroom.
About Experimental Biology 2022
Experimental Biologyis the annual meeting of five societies that explores the latest research in physiology, anatomy, biochemistry and molecular biology, investigative pathology and pharmacology. With a mission to share the newest scientific concepts and research findings shaping clinical advances, the meeting offers an unparalleled opportunity for global exchange among scientists who represent dozens of scientific areas, from laboratory to translational to clinical research.
About the American Physiological Society
Physiology is a broad area of scientific inquiry that focuses on how molecules, cells, tissues and organs function in health and disease. The American Physiological Society connects a global, multidisciplinary community of more than 10,000 biomedical scientists and educators as part of its mission to advance scientific discovery, understand life and improve health. The Society drives collaboration and spotlights scientific discoveries through its 16 scholarly journals and programming that support researchers and educators in their work.
Related Content
- The Physiologist Magazine
- APS Launches CEO Search in Partnership with Russell Reynolds Associates
- Mary E. Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell, Shimon Sakaguchi Named 2025 Nobel Laureates in Physiology or Medicine
- Viewing a Hot Virtual Environment Helps the Body Cool Off During Exercise
- APS Selects JPA Health to Lead Strategic Communications Campaign Elevating Physiology’s Vital Role
- Drinking Less Fluids May Increase Stress Hormone Levels
- Scott Steen to Retire as CEO of the American Physiological Society
 Media Inquiries
Media Inquiries
Contact the Communications Department to:
- Interview a scientific expert.
- Request a study or journal article.
- Get background and resources on physiology.
Email communications@physiology.org or call 301.634.7314.

